The Importance of Accuracy in Physics
Physics, as a fundamental science, relies heavily on the concept of accuracy. The precision and correctness of measurements and calculations are crucial in understanding the natural world and making reliable predictions.
Accuracy in physics ensures that experimental results are trustworthy and reproducible. It allows researchers to validate theories, test hypotheses, and push the boundaries of scientific knowledge. Without accurate data, the foundations of physics would be shaky at best.
One key aspect of accuracy in physics is the use of precise instruments for measurement. From rulers and stopwatches to sophisticated particle detectors and telescopes, the tools used by physicists must provide reliable data to draw meaningful conclusions.
In addition to instrumentation, mathematical calculations play a vital role in ensuring accuracy. Errors in calculations can propagate and lead to significant discrepancies in results. Therefore, physicists must pay close attention to detail and perform rigorous checks to maintain accuracy throughout their work.
Moreover, accurate data enables physicists to make informed decisions when designing experiments or interpreting results. It allows them to identify patterns, establish relationships between variables, and uncover new phenomena that may have gone unnoticed otherwise.
In conclusion, accuracy is not just a desirable trait in physics – it is an absolute necessity. By prioritising precision and correctness in their work, physicists can continue to unravel the mysteries of the universe with confidence and clarity.
Understanding Accuracy in Physics: Key Questions Answered
- What is accuracy of measurement in physics?
- What is accuracy and precision in physics?
- What is simple definition of accuracy?
- What is accuracy and errors?
What is accuracy of measurement in physics?
In the realm of physics, the concept of accuracy of measurement holds paramount importance. Accuracy in physics refers to the degree of closeness between a measured value and the true value of a physical quantity. It signifies how well an experimental result reflects the actual value being measured, providing insights into the reliability and validity of scientific data. Achieving high accuracy in measurements involves minimising errors and uncertainties through meticulous calibration, precise instrumentation, and rigorous data analysis. By understanding and striving for accuracy in measurements, physicists can enhance the credibility of their findings, validate theories, and advance our understanding of the natural world with confidence and precision.
What is accuracy and precision in physics?
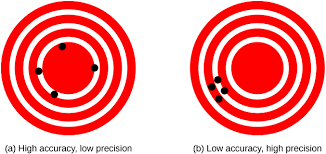
In the realm of physics, accuracy and precision are fundamental concepts that play a crucial role in the reliability of experimental results and theoretical predictions. Accuracy refers to how close a measured value is to the true or accepted value of a quantity. It reflects the absence of systematic errors in measurements and indicates the correctness of the data obtained. Precision, on the other hand, relates to the consistency and reproducibility of measurements. It assesses the degree of scatter or variation in multiple measurements of the same quantity. In physics, achieving both high accuracy and precision is essential for building robust theories, validating experimental outcomes, and advancing scientific understanding with confidence and rigour.
What is simple definition of accuracy?
In the realm of physics, accuracy refers to the degree of closeness between a measured or calculated value and the true value of a quantity. In simpler terms, accuracy in physics is all about how close a measurement or result is to the actual, correct value it represents. This concept is essential for ensuring the reliability and validity of experimental data and theoretical predictions in physics. Maintaining high levels of accuracy allows physicists to draw meaningful conclusions, validate theories, and make informed decisions based on precise information.
What is accuracy and errors?
In the field of physics, accuracy refers to the degree of closeness between a measured or calculated value and the true value of a quantity. It is essential to distinguish between accuracy and precision, with accuracy focusing on how close a measurement is to the actual value, while precision relates to the consistency of repeated measurements. Errors in physics can arise from various sources, such as limitations in measurement instruments, human mistakes, environmental factors, or inherent uncertainties in physical phenomena. Understanding and quantifying these errors are crucial for ensuring that experimental results are reliable and meaningful in advancing scientific knowledge. By acknowledging and addressing errors, physicists can strive for greater accuracy in their observations and interpretations of the natural world.