Understanding the Difference Between Accuracy and Precision
Accuracy and precision are two terms commonly used in various fields, from science and engineering to statistics and measurement. While they may seem similar, they have distinct meanings and play crucial roles in determining the quality and reliability of data or measurements. Let’s delve into the differences between accuracy and precision.
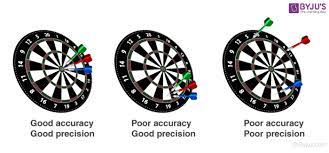
Accuracy refers to how close a measured value is to the true or target value. In other words, it measures the correctness or trueness of a measurement. For example, if you were aiming at a bullseye on a target, accuracy would be achieved if your arrow hits the center consistently. The more accurate your measurements are, the closer they are to the actual value you are trying to determine.
Precision, on the other hand, relates to how consistent or reproducible a set of measurements is when repeated under similar conditions. It focuses on the consistency of results rather than their correctness. In our bullseye analogy, precision would be achieved if all your arrows hit closely together but not necessarily at the center of the target. Precision reflects the level of detail or resolution in your measurements.
To further illustrate these concepts, let’s consider an example involving weight measurements. Imagine you have a weighing scale that is slightly misaligned and always shows a weight that is 0.5kg more than the actual weight. If you weigh an object several times using this scale and consistently get readings that are 0.5kg higher than its true weight, then your measurements are precise but not accurate.
Conversely, if you use another scale that consistently shows weights 2kg lower than their true values but provides consistent readings for each object you weigh, then your measurements are precise but not accurate as well.
Ideally, we aim for both accuracy and precision in any measurement or data collection process. Achieving both ensures reliable results that can be trusted for decision-making or further analysis.
In scientific experiments or engineering projects, accuracy and precision are vital for ensuring the validity of findings or the quality of products. In statistical analysis, precision is often used to measure the variability or spread of data, while accuracy is used to assess bias or systematic errors.
It’s important to note that accuracy and precision are not mutually exclusive. You can have measurements that are both accurate and precise, where the values closely match the true value, and the results are consistent. However, it’s also possible to have measurements that are accurate but not precise (or vice versa) or even neither accurate nor precise.
In conclusion, accuracy refers to how close a measured value is to the true value, while precision relates to the consistency or reproducibility of measurements. Both accuracy and precision play crucial roles in determining the reliability and quality of data or measurements. Understanding these differences is essential for making informed decisions based on collected data and ensuring trustworthy results in various fields of study.
Understanding the Distinction: Frequently Asked Questions about Accuracy and Precision in English (UK)
- What is the difference between precision and accuracy in table?
- What is difference between accuracy and precision with example?
- What is the difference between accuracy and precision Class 10?
- Which means precision?
What is the difference between precision and accuracy in table?
In the context of tables, the terms precision and accuracy can be used to describe the quality or reliability of the data presented. Here’s how they differ:
Precision in a table refers to the level of detail or specificity in the data. It indicates how many decimal places or significant figures are included in the values. A table with high precision will display data with more decimal places, providing a more detailed representation of the measurements or quantities. For example, a table showing temperature measurements with precision up to two decimal places (e.g., 25.56°C) is considered more precise than a table that only displays whole numbers (e.g., 26°C).
Accuracy in a table, on the other hand, refers to how close the presented values are to their true or target values. It measures whether the data accurately reflects reality or matches expected values. An accurate table will provide measurements that are close to their actual values, minimizing errors or discrepancies between what is recorded and what is expected.
To illustrate this further, let’s consider an example involving a scientific experiment measuring liquid volumes. If a table presents volume measurements with high precision (e.g., 50.234 mL), but all values consistently deviate from their true values by 5 mL, then the table is precise but not accurate.
Conversely, if a table displays volume measurements with low precision (e.g., rounded to whole numbers), but all values align closely with their true values, then it is accurate but not precise.
Ideally, tables should strive for both accuracy and precision simultaneously. This means presenting data that is both close to its true value and displayed with an appropriate level of detail or specificity.
In summary, when discussing tables, precision refers to the level of detail or number of decimal places in the presented data, while accuracy relates to how closely those values match their true or expected counterparts. Both precision and accuracy contribute to ensuring reliable and trustworthy information within a table.
What is difference between accuracy and precision with example?
To better understand the difference between accuracy and precision, let’s consider an example involving a target and archery.
Accuracy: Imagine you are an archer aiming at a bullseye target. Accuracy refers to how close your arrow hits the center of the target, which represents the true or desired value. If your arrows consistently hit the center of the bullseye, you have high accuracy. This means your measurements or actions are correct and aligned with the intended target.
Precision: Now, let’s consider a scenario where your arrows consistently hit close together but not necessarily at the center of the target. Precision refers to how consistent or reproducible your results are when repeated under similar conditions. In this case, even though your arrows may not hit the bullseye every time, they cluster tightly together on the target. This indicates high precision because your measurements or actions are consistent and reproducible.
To summarize:
– Accuracy is about how close your results are to the true value or target.
– Precision is about how consistent or reproducible your results are when repeated.
In our archery example:
– High accuracy would mean hitting the center of the bullseye consistently.
– High precision would mean hitting close together in a tight cluster, even if not on the bullseye every time.
It’s important to note that accuracy and precision are independent of each other. You can have measurements that are accurate but not precise (hitting off-center but consistently in one area), precise but not accurate (hitting tightly clustered away from the center), both accurate and precise (hitting dead center consistently), or neither accurate nor precise (randomly scattered hits).
In various fields like science, engineering, manufacturing, and statistics, both accuracy and precision play crucial roles in ensuring reliable data collection, measurements, product quality control, experimental validity, statistical analysis, and decision-making processes.
What is the difference between accuracy and precision Class 10?
In the context of Class 10 education, the difference between accuracy and precision can be explained as follows:
Accuracy refers to how close a measured value is to the true or accepted value. It is a measure of correctness. For example, if you are conducting an experiment to determine the length of an object, accuracy would mean obtaining a measurement that is very close to the actual length. In other words, it measures how well your result matches the expected or correct value.
Precision, on the other hand, relates to how consistent or reproducible a set of measurements is when repeated under similar conditions. It focuses on the consistency of results rather than their correctness. Precision indicates how well you can repeat a measurement and obtain similar values each time. For example, if you perform multiple measurements of an object’s length and consistently get results that are very close to each other (even if they are not exactly correct), then your measurements are precise.
To better understand this distinction, consider an analogy using darts. Accuracy would be hitting the bullseye consistently with your throws, regardless of whether they cluster tightly together or not. Precision would be hitting very close to each other but not necessarily at the bullseye every time.
In summary, accuracy refers to correctness or how close a measured value is to the true value, while precision refers to consistency or reproducibility in obtaining similar results. Both accuracy and precision are important in scientific experiments and data analysis as they help assess reliability and validity of measurements.
Which means precision?
Precision refers to the level of consistency or reproducibility in a set of measurements when repeated under similar conditions. It focuses on the degree of detail or resolution in the measurements rather than their correctness. In other words, precision reflects how closely together a series of values or results are, indicating the level of variability or spread in the data. A high level of precision means that the measurements are tightly clustered around each other, while low precision indicates greater variability or scatter in the measurements.